What is sinus lifting?
A sinus lift, also known as sinus augmentation, is a surgical procedure designed to increase the amount of bone in the upper jaw, specifically in the area of the molars and premolars, by adding bone material to the maxillary sinus region. This procedure can be performed using two main techniques:
- External Sinus Lifting: A small window is created in the bone to directly lift the sinus membrane. Used when significant bone height is needed.
- Internal Sinus Lifting: Less invasive, involves lifting the sinus membrane through the implant site. Suitable for minor bone height increases.
Both methods aim to create enough bone height and density to support the placement of dental implants.
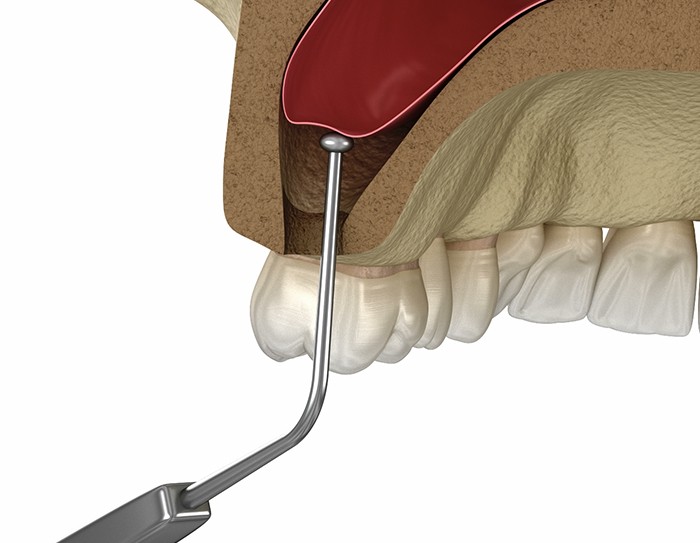
Why do you need sinuses lifted?
- Insufficient Bone for Implants: Increases bone height in areas where natural bone is inadequate.
- Bone Loss: Restores lost bone from periodontal disease or tooth loss.
- Naturally Large Sinuses: Repositions the sinus floor to make room for implants in cases of large sinuses.
- Preparation for Implants: Ensures a secure foundation for dental implants in the upper jaw.
What does the procedure look like?
- Preparation and Imaging: X-rays or CT scans are used to assess the sinuses and bone structure, determining the exact approach and amount of bone needed.
- External Sinus Lifting:
- Local Anesthesia: Administered for comfort during the procedure.
- Access: Incision is made in the gum tissue above the missing teeth. A window is created in the bone to access the sinus cavity.
- Membrane Lifting: Sinus membrane is gently lifted, and bone graft material is added to the space.
- Closure: Incision is sutured, and healing occurs over several months.
- Internal Sinus Lifting:
- Access Through Implant Site: Sinus membrane is accessed and lifted through the implant cavity.
- Bone Grafting: Bone graft material is added, and implants are often placed simultaneously.
What are the risks involved?
- Sinus Infection: Manipulation of the sinus cavity may lead to infection, causing discomfort or congestion.
- Sinus Membrane Perforation: Membrane tearing may occur but can often be repaired during the procedure.
- Bone Graft Rejection: Rarely, the bone graft material may not integrate properly, requiring a repeat procedure.
- Swelling and Discomfort: Temporary swelling, bruising, or mild pain may occur but typically resolves within a few days.
- Bleeding: Normal during healing, but excessive bleeding is a potential risk.
- Implant Failure: If the bone graft does not integrate, implants may fail, requiring additional treatment.