What is tooth extraction?
Tooth extraction is a dental procedure that involves removing a tooth from its socket in the bone. It is typically performed when a tooth is severely damaged, decayed, or poses a risk to the surrounding teeth and gums. Extractions can be simple or surgical, depending on the complexity of the situation.
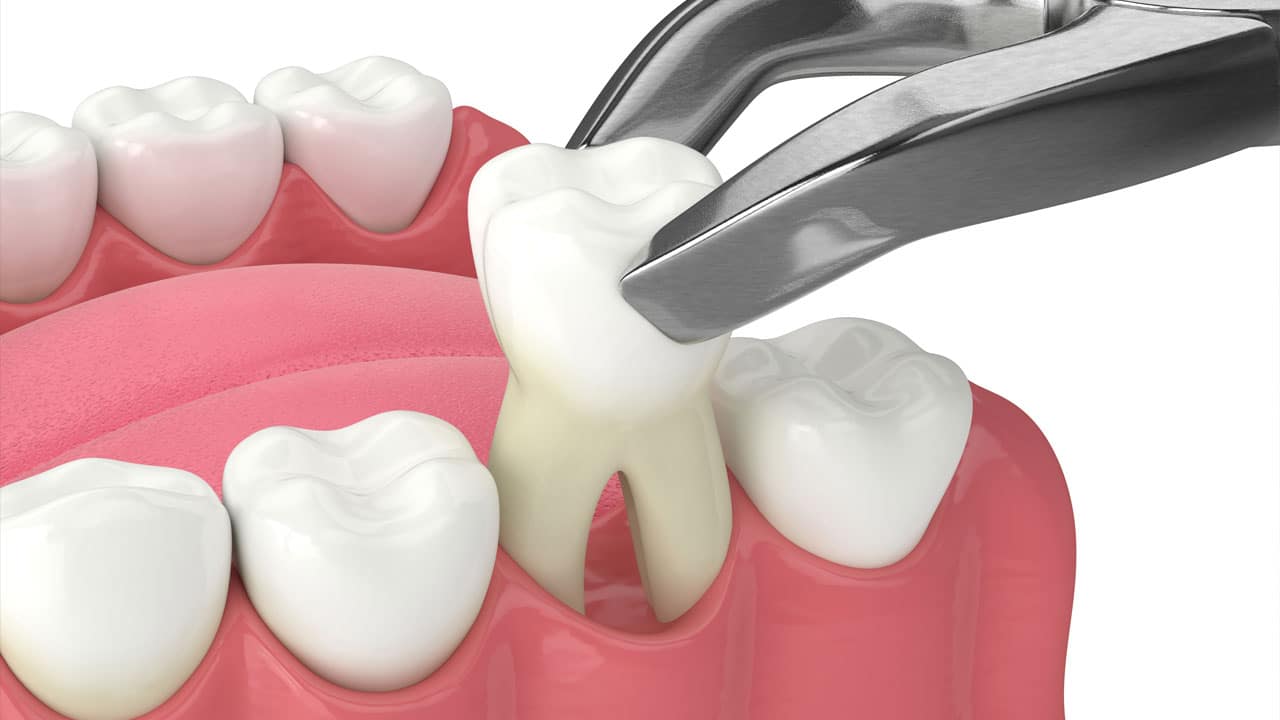
What types of tooth extractions are available?
- Simple Extraction: Performed on a visible tooth above the gum line and removed without complications.
- Surgical Extraction: A more complex procedure used for teeth broken at the gum line or impacted teeth. May involve incisions or sectioning the tooth into smaller pieces for removal.
What are the reasons to extract a tooth?
- Severe Tooth Decay or Infection: When a tooth is too damaged to restore, extraction prevents further damage.
- Impacted Teeth: Wisdom teeth often require removal to avoid pain, infection, or damage to other teeth.
- Overcrowding: Teeth may be extracted to create space before orthodontic treatments.
- Periodontal (Gum) Disease: Severely loosened teeth due to gum disease may need extraction.
- Fractured Teeth: Teeth broken below the gum line may require removal if they cannot be repaired.
- Prevention of Complications: Proactive extractions may be done for teeth likely to cause future issues, such as wisdom teeth.
What does the procedure look like for tooth extraction?
- Examination and Preparation: Dentist examines the tooth and takes X-rays to assess its condition. Local anesthesia is administered.
- Simple Extraction: Tooth is loosened using an elevator, and forceps are used to remove it from the socket.
- Surgical Extraction: Involves making an incision in the gum to access the tooth. Bone may be removed, and the tooth may be sectioned for easier removal.
- Post-Extraction Care: Dentist places gauze over the site to control bleeding and provides instructions for aftercare, such as avoiding certain foods and rinsing with salt water.
What are the risks involved?
- Dry Socket: Occurs if the blood clot is dislodged, exposing the bone and nerves, leading to pain and delayed healing.
- Infection: Though rare, infection can occur. Signs include swelling, fever, and persistent pain.
- Excessive Bleeding: Prolonged bleeding may happen, especially in patients with clotting disorders or on blood-thinning medications.
- Nerve Damage: Rare but possible during surgical extractions, causing temporary or permanent numbness.
- Sinus Issues: Upper jaw extractions can sometimes create an opening into the sinus cavity, requiring additional treatment.
- Jaw Fracture: In rare cases, severe impaction or weak bones can lead to a jaw fracture during extraction.